
CaMKKβ regulates proliferation, apoptosis, and glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma via PI3K/AKT pathway
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common types of cancer and ranks second in cancer-related deaths globally (1). In recent years, 700,000 people worldwide have died each year as a result of HCC (2). Presently, surgical resection, orthotopic liver transplantation, radiofrequency ablation, and other current methods have the limitations of high recurrence rate and poor prognosis (3-5). Since most cases of HCC are diagnosed at an advanced stage, surgery is not a suitable treatment approach (6). Molecular targeted therapy is another treatment, but current targeted drugs, such as sorafenib, regorafenib, and cabozantinib, are limited, and all have toxic side effects (7-9). Therefore, low cytotoxic drug targets are urgently needed for HCC chemotherapy.
The second messenger in the cell is Ca2+, and it plays a vital role in the signaling pathway of the cell (10). Changes in Ca2+ concentration regulate biological processes such as cell proliferation and apoptosis, cell cycle, and gene transcription (11-14). When it is stimulated, Ca2+ concentration increases and Ca2+ channels are activated (15). Studies have shown that disruption of normal Ca2+ signaling is associated with tumor progression (16). Calmodulin (CaM) is a sensor of Ca2+ concentration. The Ca2+ binds to CaM, causing changes in the conformation of CaM and enhancing the affinity of CaM kinase (CaMKK, CaMKI, CaMKII, and CaMKIV) to CaM. The protein kinase CaMKK has a multifunction that is encoded by CAMKK1 and CAMKK2 genes to produce calcium ions/calmodulin stimulated protein kinase kinases α (CaMKK) protein or calcium ions/calmodulins stimulated protein kinase kinases β (CaMKKβ) protein, respectively (17). One action of CaMKK is to phosphorylate CaMKI and CaMKIV, and AMPK and PKB/Akt (18,19). The signaling pathway formed by CaMKK, CaMKI, and CaMKIV is known as the Ca2+/cam-dependent kinase cascade, and is related to cell proliferation and apoptosis (20). These kinases are widely present in a variety of cancer types, and control various cancer-related functions (21). Their potential as intervention targets for anticancer therapy has been recognized.
In this study, we established stable silent CaMKKβ-HCC cells and restored the function of the culture by adding AKT overexpression plasmids. Our results demonstrated for the first time that CaMKKβ knockdown partially inhibited HCC cell proliferation and glycolysis and promotes apoptosis through inactivation PI3K/Akt1 signaling.
We present the following article ARRIVE in accordance with the ARRIVE reporting checklist (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/apm-20-1789).
Methods
Cell culture
We purchased HepG2 cells from the Shanghai Academy of Sciences Cell Bank. The HepG2 cells were incubated in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) (Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) at 37 °C, 5% CO2.
Cell transfection
The three groups of shRNA selected were shRNA1, shRNA2, and shRNA3, and were chosen to interfere with CaMKKβ gene. The interference efficiency was tested by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The specific short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) were cloned into the GV248 lentivirus green fluorescent overexpression vector (GenePharma, Shanghai, China). GV248 lentivirus green fluorescent empty vector (without cloning shRNAs) was used as a negative control. Lentivirus plasmids by Lipofectamine®2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) were used to transfect the HepG2 cells. After transfection for 48 h, the supernatant containing lentivirus was collected and concentrated to calibrate the viral titer. The final concentration of lentivirus was 4×108 TU/mL, and was stored at −80 °C.
RT-qPCR
Total RNA was extracted from cells and tissues with TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The RT-qPCR reaction was performed with Quant One Step RT-qPCR Kit (TIANGEN, Beijing, China) by using the ABI7500 (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA). The thermocycling parameters were as follows: a holding step at 95 °C 30 sec, and 40 cycles at 95 °C 5 sec and 60 °C 30 sec. Primers were as follows: CaMKKβ, forward 5'-TCAAACCTTCCAACCTCCTG-3', reverse 5'-TTGCTCACACCAAAGTCAGC-3'; LDHA, forward 5'-GCACGTCAGCAAGAGGGAGAAAG-3', reverse 5'-AGGTAACGGAATCGGGCTGAA-3'; β-actin, forward 5'-CTTCTACAATGAGCTGCGTG-3', reverse 5'-TCATGAGGTA GTCAGTCAGG-3'. CT value was normalized to Actin and calculated with the 2-ΔΔCt.
Cell proliferation assay
The HepG2 cells were cultured in 96-well plates with 5×103 cells per well. Cells were incubated for another 48 h. Then, 10 µL of MTT solution was added to each well and was further incubated for 4 h at 37 °C. The reaction was then finished with 100 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and the absorbance was measured at 490 nm on a Multiskan FC microplate reader (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA).
Hoechst 33258 staining
The apoptotic morphology was observed by Hoechst 33258 (G3680, Solarbio, Beijing, China) staining. Cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde for 10 min. Then, cells were stained by 10 mg/L of Hoechst 33258 for 1 h. The color images were observed by an ECLIPSE Ti microscope.
Flow cytometry
The HepG2 cells were digested with trypsin (Solarbio, Beijing, China), and fixed overnight at 4 °C with 70% ethanol. Then, 10 mg/mL RNaseA (Solarbio, Beijing, China) and propidium iodide (PI) (Solarbio, Beijing, China) were added and stained overnight at 4 °C. A Cell Cycle and Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China) was used to detect the cell DNA content and apoptotic rate using flow cytometry (Becton, Dickinson, and Co., Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Annexv-fitc(−)/PI(−) (lower left) is normal, Annexv-Fitc(+)/PI(−) cells (lower right) are early apoptotic, and Annexv-Fitc(+)/PI(+) (upper right) are late apoptotic. AnnexinV(−)/PI(+) (upper left) is necrotic cell.
Cell invasion assay
Invasion assay of HepG2 cell was handled with Trans-well chamber (6.5 mm, Corning, USA) as previous reported (22). Shortly, cell suspensions (5×104/100 mL) were added to a matrigel-covered (1 mg/mL, BD, USA) membrane, and the upper and lower compartment was filled with 600 µL NIH-3T3-conditioned medium with FBS. 24 hours later, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and then stained with crystal violet. The number of cells was scored visually in five random fields for microscopic observation.
Detection of glucose and lactate concentrations
According to the manufacturer’s instruction, the glucose and lactate concentrations in the medium were measured using the glucose detection kit (Nanjing Jiancheng, China) and the lactate detection kit (Nanjing Jiancheng, China). The absorbance glucose consumption was measured at 570 nm using a multifunctional microporous plate reader (BioTek, USA). The glucose consumption is equal to the initial glucose concentration in DMEM (450 mg/dL) minus the glucose concentration in the medium after transfection.
Enzyme activity analysis
HepG2 cells were digested with 0.25% trypsin (Sigma, USA), centrifuged for 5 minutes at 1,000 g, followed by dissolving in a 300 w ultrasonic machine. The supernatant then was collected and the protein concentrations in each sample were quantitatively analyzed using a specific gold cholic acid (BCA) protein quantification kit (Beyotime, China). Hexokinase (HK), pyruvate kinase (PK), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzymatic activity were measured using an HK assay kit (A077-1, Nanjing Jiancheng, China) and PK asasy kit (A076-1, Nanjing Jiancheng, China), and LDH asasy kit (A076-1, Nanjing Jiancheng, China), respectively, in accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction. All values were normalized to total protein level.
TUNEL assay
According to the manufacturer’s instructions, a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China) was used to measure the apoptosis in tumor tissues. The result was observed under an ECLIPSE Ti microscope.
Immunohistochemistry
Dewaxed and hydrated paraffin sections were sealed with 5% normal goat serum for 1 h. Then, paraffin sections were co-cultured with the antibodies Ki67 (ab15580, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) and LDHA (ab84716, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) overnight at 4 °C. Sections were then washed with tris buffered saline + tween 20 (TBST) and incubated with SignalStain® Boost immunohistochemistry (IHC) Detection Reagent (#8114, CST, Danvers, MA, USA) for 30 min at room temperature. The result was observed under an optical microscope.
Western blots assay
Proteins extracted from cells or tissues were separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) (Solarbio, Beijing, China) and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Solarbio, Beijing, China). Membranes were blocked by 5% skim milk. Then, proteins were incubated with the primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C. The primary antibodies were as follows: CaMKKβ (ab177255, Abam, UK), Ki67 (ab243878, Abcam, UK), PCNA (#2586, 1:1,000, CST, USA), Survivin (#2808, 1:1,000, CST, USA), cleaved Caspase-3 (#9660, 1:1,000, CST, USA), cleaved Caspase-9 (#9508, 1:1,000, CST, USA), E-Cadherin (ab1416, 1:50, Abcam, UK); N-cadherin (ab18203, 1:600, Abcam, UK); Vimentin (ab8978, 1:600, Abcam, UK), HK2 (ab209847, 1:1,000, Abcam, UK), PKM2 (ab137852, 1:500, Abcam, UK), LDHA (ab84716, 1:500, Abcam, UK), PI3K (ab32089, 1:1,000, Abcam, UK), p-PI3K (ab191606, 1:1,000, Abcam, UK), AKT (ab8805, 1:500, Abcam, UK), and p-AKT (ab38449, 1:500, Abcam, UK). Next, the samples were washed with PBS and incubated with anti-rabbit IgG (Solarbio, Beijing, China) and anti-biotin horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-linked antibody (Solarbio, Beijing, China) for 1 h. The bands were visualized with the enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) detection kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China).
Animal models
We purchased 20 male, 7-week old BALB/c nude mice from Beijing Weitong Lihua Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd. Animals were housed in a controlled environment at 25±3 °C, humidity 60%, in a cycle with 12 h light/dark. The mice had unrestricted access to food and water. Transfection of HepG2 cells with shRNA was performed by subcutaneous injection into the right thigh to form xenograft tumors. The mice were divided into two groups (n=8): control group, and CaMKKβ-shNRA group. Tumor volume was measured every 5 days until 30 days. Mice were euthanized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium (200 mg/kg body weight). Tumors were harvested for subsequent experiments. All animal experiments were approved by the ethics committee of Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College (No. 2020053) and performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted with SPSS 21.0 (SPSS, Inc., IBM, Chicago, IL, USA). Data were expressed as mean ± SD. The data were analyzed using t-test and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Statistical significance was set at P<0.05.
Results
shRNAs interference efficiency detection
In this study, the three kinds of shRNA, shRNA1, shRNA2, and shRNA3, were transfected into HepG2 cells to interfere with the CaMKKβ gene. The results of RT-PCR results showed that the mRNA levels of CaMKKβ were significantly reduced in all three shRNA groups (Figure 1A), and that CaMKKβ-shRNA1 was the most efficient in this respect. Similarly, WB results showed that all three groups of shRNAs reduced CaMKK protein levels, and CaMKK shRNA1 was the most effective (Figure 1B). Since the interference efficiency of shRNA1 was the greatest, we selected CaMKKβ-shRNA1 for the follow-up experiments.
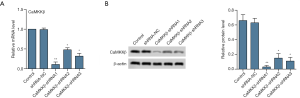
CaMKKβ knockdown interfered the proliferation and cell cycle of HepG2 cells
Results from MTT (Figure 2A) indicated that, compared with the control group, the cell viability of CaMKK shRNA1 group was greatly lower. And clone formation (Figure 2B) assay demonstrated that the clone formation rate of CaMKKβ-shRNA1 was significantly lower than that of the control group. WB data showed that the expressions of proliferation-related proteins Ki67 and PCNA were significantly decreased in the CaMKKβ-shRNA1 group compared with the control group (Figure 2C). Flow cytometry analysis showed that CaMKKβ-shRNA1 treatment significantly increased the percentage of G0/G1 phase cells and decreased the percentage of S-phase cells in HepG2 cells (Figure 2D,E).
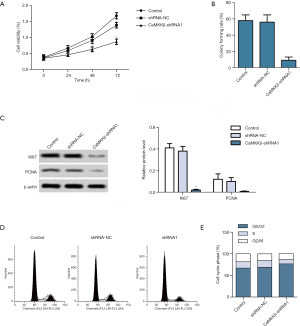
CaMKKβ knockdown prompted the apoptosis of HepG2 cells
Hoechst staining demonstrated that, the CaMKKβ-shRNA1 group showed denser and heavily stained apoptotic cells compared with the control (Figure 3A). Flow cytometry showed that the apoptosis rate of CaMKKβ-shRNA1group was significantly higher than that of the control group (Figure 3B). Moreover, Western blotting showed that the expression of apoptosis suppressor Survivin in CaMKKβ-shRNA1 group was inhibited, while the expression of apoptosis-related proteins Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 was significantly enhanced, compared with the control group (Figure 3C). The above experimental results demonstrated that CaMKKβ interference accelerated the apoptosis of Hep2 cells.
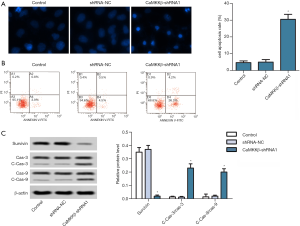
CaMKKβ knockdown inhibited invasion and EMT of HepG2 cells
Next, we determined the effect of CaMKKβ knockdown on cell invasion in vitro. Invasion assay indicated that CaMKKβ knockdown significantly interfered with cell invasion relative to the untreated control group (Figure 4A). EMT is widely regarded as the key process of tumor invasion and metastasis (23), EMT-related markers (E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and Vimentin) were detected using western blot in HepG2 cells. Compared with the control group, CaMKKβ knockdown remarkably increased the protein expression of E-cadherin, but decreased the expression of N-cadherin and Vimentin (Figure 4B).
CaMKKβ knockdown inhibited HepG2 cells glycolysis
By exploring the effect of CaMKKβ expression on the glucose metabolism of HepG2 cells, we found that compared with the control group, CaMKKβ knockdown in HepG2 cells greatly inhibited its glycolytic activity, such as reducing glucose uptake (Figure 5A) and lactate release (Figure 5B). Enzyme activity test results showed that the key glycolysis rate-limiting enzymes HK, PK and LDH are significantly lower (Figure 5C). Western blot analysis showed that the protein expression of HK2, PKM2, and LDHA in HepG2 cells were significantly reduced (Figure 5D).
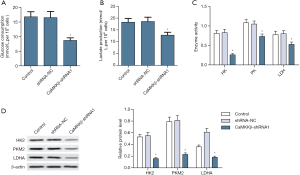
CaMKKβ knockdown mediated proliferation, apoptosis, and glycolysis of HepG2 cells PI3K/AKT pathways
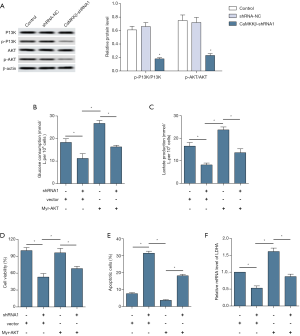
Furthermore, the potential role of PI3K/AKT signaling in the anticancer activity of CaMKKβ knockdown was examined. Western blot analysis showed that CaMKKβ knockdown significantly decreased the phosphorylation levels of PI3K and AKT, compared to control group (Figure 6A). To further explore whether CaMKKβ regulate proliferation, apoptosis, and glycolysis of HCC cells through PI3K/AKT pathways, AKT overexpression plasmid (pT3-myr-AKT-HA, AddGene, USA) was added to HepG2 cells to assess changes in proliferation, apoptosis, and glycolysis. The results showed that the decreased glucose consumption (Figure 6B) and lactic acid production (Figure 6C) recovered significantly after AKT plasmid transfection. Notely, overexpression of active Akt significantly increased the viability (Figure 6D) and inhibited apoptotic response (Figure 6E) and LDHA expression (Figure 6F).
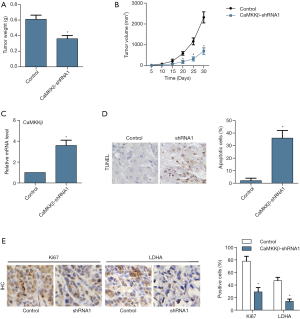
CaMKKβ knockdown inhibited tumor enlargement in xenograft tumor mice
In present study, we did xenograft tumor mice experiment. After 20 days of HepG2 cell injection, the tumor tissue size of the CaMKKβ-shRNA1 group start to be significantly inhibited than that of the control group. And as time went on, the difference in tumor size between the two groups became more and more obvious, and the tumor weight (Figure 7A) and size (Figure 7B) of the CaMKKβ-shRNA1 group was significantly blocked. The mRNA level of CaMKKβ was significantly lower in the CaMKKβ-shRNA1 group than that in the control group (Figure 7C). TUNEL assay showed that apoptotic cells increased more significantly in the CaMKKβ-shRNA1 group than in the control group (Figure 7D). In the IHC assay, the expression of proliferation-related factor Ki67 and glycolytic restriction enzyme LDHA were decreased in the tissue of the CaMKKβ-shRNA1 group, both of which compared with that in the control group (Figure 7E).
Discussion
Studies have shown that CaMKKβ expression is limited in normal tissues, but it is overexpressed in tumor tissues of certain cancers (24-26). The expression of CaMKKβ was significantly up-regulated in HCC and negatively correlated with the survival of HCC patients. CaMKKβ protein is highly expressed in a variety of HCC cell lines and is significantly up-regulated compared to normal primary HCC (27). To assess how CaMKKβ regulate important biological processes of HCC, we knock out CaMKKβ expression in HepG2 cells. we found that CaMKKβ knockdown promoted glycolysis in HepG2 cells through PI3K/AKT pathways and regulated cell proliferation and apoptosis. Furthermore, the in vivo experiment also showed that CaMKKβ knockdown limited glycolysis and HCC growth. This finding confirmed the results of previous studies that CaMKKβ might inhibit the occurrence of HCC.
CaMKKβ was overexpressed in a variety of tumor cell types in vitro, which affected the proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells. It has previously been reported that CAMKKβ regulates cell proliferation in high-grade glioma samples (28). CaMKKβ was overexpressed in LNCaP of prostate cancer cells to increase cell migration (24). In contrast, the down-regulation of CaMKK expression induced by RNA interference or drug inhibition inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells (29). By inhibiting the high expression of CaMKKβ in HepG2 cells, we found that the down-regulation of CaMKKβ resulted in the inhibition of cell proliferation, and the expression of proliferation-related proteins Ki67 and PCNA were significantly inhibited. Similarly, inhibition of CaMKKβ activity in HepG2 cells suggested that down-regulation of CaMKKβ expression promoted apoptosis. Survivin expression, which inhibits apoptosis, was down-regulated, while the pro-apoptotic Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 expressions were up-regulated. In vivo experimental results of transplanted tumor mice further confirmed that CaMKKβ interference blocked the proliferation of HCC and promoted its apoptosis.
The increase of glycolysis in tumor cells provides energy for the growth of tumor cells, and the intermediate metabolites of glycolysis can provide raw materials for tumor cell proliferation (30). Therefore, glycolysis is closely related to cell proliferation and apoptosis (31). In this study, we found that CaMKKβ knockdown in HepG2 cells not only led to changes in glycolysis, also cell proliferation and apoptosis. Many enzymes in the glycolytic pathway are upregulated by carcinogens, which play an important role in triggering aerobic glycolysis and its toxicity. Rády et al. reported that CFLP mice treated with aflatoxin B1 enhanced intraperitoneal HK, PFK, PK and LDH activities 28 days after administration (32). In addition, the food-borne mycotoxin ferric acid up-regulates several glycolytic enzymes including PDK1, PKM2 and LDHa to convert energy metabolism from mitochondrial processes to glycolysis in human HepG2 cells (33). Like this, our results also showed that, after treating HepG2 cells for 72 hours, CaMKKβ knockdown increased the activity and protein levels of HK, PK and LDH.
The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is related to a variety of human malignant tumor biological processes, such as cell adhesion, growth, invasion, and angiogenesis (34,35). The PI3K/AKT pathway is one of the most common activation pathways in cancers, and it is of great significance in regulating glucose metabolism, proliferation and apoptosis of tumor cells (36). Akt plays a role in the anti-apoptotic pathway through phosphorylation of downstream target proteins. Continuous activation of AKT can prevent PTEN-mediated apoptosis by phosphorylation of Bad (Bcl-2 family member) and protease Caspase-9. in addition, AKT also regulates cell proliferation by mediating the cell cycle. Nevertheless, it has not been tested whether CaMKKβ regulates glycolysis in HCC cells through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Our research showed that, after establishing silenced CaMKKβ-HepG2 cells, CaMKKβ knockdown inhibited glycolysis in HepG2 cells through the PI3K/AKT pathway, and regulated cell proliferation and apoptosis.
In summary, CaMKKβ knockdown regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, and glycolysis in HepG2 cells through the PI3K/AKT pathway, accordingly inhibiting the occurrence and development of HCC. This study has some limitations, such as upstream events leading to CaMKKβ down-regulation in HCC and the specific molecular binding mechanism of CaMKKβ to regulate PI3K/AKT pathway is still unclear and needs further study.
Acknowledgments
This article thanks the Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College for its support.
Funding: None.
Footnote
Reporting Checklist: The authors have completed the ARRIVE reporting checklist. Available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/apm-20-1789
Data Sharing Statement: Available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/apm-20-1789
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/apm-20-1789). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All animal experiments were approved by the ethics committee of Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College (No. 2020053) and performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Open Access Statement: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), which permits the non-commercial replication and distribution of the article with the strict proviso that no changes or edits are made and the original work is properly cited (including links to both the formal publication through the relevant DOI and the license). See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
References
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016;66:7-30. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 2015;136:E359-E386. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Yin X, Hua T, Liang C, Chen Z. Efficacy of re-resection versus radiofrequency ablation for recurrent Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0/A hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after resection for primary HCC. Transl Cancer Res 2019;8:1035-45. [Crossref]
- Kakodkar R, Soin AS. Liver transplantation for HCC: A review. Indian J Surg 2012;74:100-17. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Kow AWC. Transplantation versus liver resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;4:33. [Crossref]
- El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2008;134:1752-63. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Boland P, Wu J. Systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: beyond sorafenib. Chin Clin Oncol 2018;7:50. [Crossref]
- Personeni N, Pressiani T, Santoro A, et al. Regorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: latest evidence and clinical implications. Drugs Context 2018;7:212533. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa GK, Meyer T, Cheng AL, et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced and progressing hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2018;379:54-63. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003;4:517-29. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Schreiber R. Ca2+ signaling, intracellular pH and cell volume in cell proliferation. J Membr Biol 2005;205:129-37. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Pinton P, Giorgi C, Siviero R, et al. Calcium and apoptosis: ER-mitochondria Ca2+ transfer in the control of apoptosis. Oncogene 2008;27:6407-18. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Dewenter M, von der Lieth A, Katus HA, et al. Calcium Signaling and Transcriptional Regulation in Cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 2017;121:1000-20. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Humeau J, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Vitale I, et al. Calcium signaling and cell cycle: Progression or death. Cell Calcium 2018;70:3-15. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Fagni L, Chavis P, Ango F, et al. Complex interactions between mGluRs, intracellular Ca2+ stores and ion channels in neurons. Trends Neurosci 2000;23:80-8. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Sang LJ, Ju HQ, Liu GP, et al. LncRNA CamK-A regulates Ca2+-signaling-mediated tumor microenvironment remodeling. Mol Cell 2018;72:71-83.e7. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski JS, Skelding KA. The multi-functional calcium/calmodulin stimulated protein kinase (CaMK) family: emerging targets for anti-cancer therapeutic intervention. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2019;12:8. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Takemoto-Kimura S, Suzuki K, Horigane SI, et al. Calmodulin kinases: essential regulators in health and disease. J Neurochem 2017;141:808-18. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Li YC, Qiao JY, Wang BY, et al. Paeoniflorin ameliorates fructose-induced insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis by activating LKB1/AMPK and AKT pathways. Nutrients 2018;10:1024. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Colomer J, Means AR. Physiological roles of the Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase cascade in health and disease. Subcell Biochem 2007;45:169-214. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Wang Y, Zhao R, Zhe H. The emerging role of CaMKII in cancer. Oncotarget 2015;6:11725-34. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Zhang P, Wang C, Ma T, et al. O-GlcNAcylation enhances the invasion of thyroid anaplastic cancer cells partially by PI3K/Akt1 pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2015;8:3305-13. [PubMed]
- Parvani JG, Gujrati MD, Mack MA, et al. Silencing beta3 integrin by targeted ECO/siRNA nanoparticles inhibits EMT and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res 2015;75:2316-25. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Frigo DE, Howe MK, Wittmann BM, et al. CaM kinase kinase beta-mediated activation of the growth regulatory kinase AMPK is required for androgen-dependent migration of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 2011;71:528-37. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Ma Z, Wen D, Wang X, et al. Growth inhibition of human gastric adenocarcinoma cells in vitro by STO-609 is independent of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta and adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. Am J Transl Res 2016;8:1164-71. [PubMed]
- Gocher AM, Azabdaftari G, Euscher LM, et al. Akt activation by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CaMKK2) in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2017;292:14188-204. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Lin F, Marcelo KL, Rajapakshe K, et al. The camKK2/camKIV relay is an essential regulator of hepatic cancer. Hepatology 2015;62:505-20. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Liu DM, Wang HJ, Han B, et al. CAMKK2, Regulated by Promoter Methylation, is a Prognostic Marker in Diffuse Gliomas. CNS Neurosci Ther 2016;22:518-24. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Fu H, He H, Han Z, et al. MicroRNA-224 and its target CAMKK2 synergistically influence tumor progression and patient prognosis in prostate cancer. Tumour Biol 2015;36:1983-91. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Wang H, Wu Q, Liu Z, et al. Downregulation of FAP suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT and Ras-ERK signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 2014;5:e1155. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Jiang X, Sun Q, Li H, et al. The role of phosphoglycerate mutase 1 in tumor aerobic glycolysis and its potential therapeutic implications. Int J Cancer 2014;135:1991. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Rády P, Arany I, Boján F, et al. Effect of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic chemicals on the activities of four glycolytic enzymes in mouse lung. Chem Biol Interact 1980;31:209-13. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Sheik Abdul N, Nagiah S, Chuturgoon AA. The neglected foodborne mycotoxin fusaric acid induces bioenergetic adaptations by switching energy metabolism from mitochondrial processes to Glycolysis in a human liver (HepG2) cell line. Toxicol Lett 2020;318:74-85. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Tan PH, Xue SA, Manunta M, et al. Effect of vectors on human endothelial cell signal transduction: implications for cardiovascular gene therapy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006;26:462-7. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Jeong SJ, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, et al. Activated AKT regulates NF-κB activation, p53 inhibition and cell survival in HTLV-1-transformed cells. Oncogene 2005;24:6719-28. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Tang KL, Tang HY, Du Y, et al. PAR-2 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biosci Rep 2019;39:31. [Crossref] [PubMed]
(English Language Editor: J. Jones)


